In Texas, where expansive rural areas and increasing suburban development prevail, efficient and environmentally friendly wastewater management systems are vital. Septic systems are a popular solution for managing wastewater in areas not serviced by municipal sewage systems. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of septic design in Texas, providing valuable insights for property owners, developers, and anyone interested in sustainable wastewater solutions.
Understanding Septic Systems
What is a Septic System?
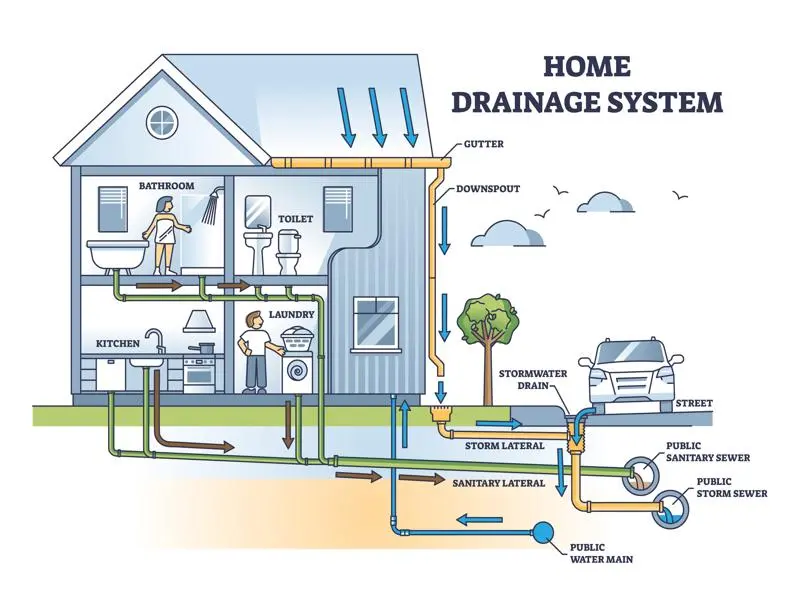
A septic system is an on-site wastewater treatment system that processes and disposes of household waste. It typically comprises a septic tank and a drain field. The septic tank separates solid waste from liquid, allowing the liquid to be dispersed and treated in the drain field.
Types of Septic Systems
There are several types of septic systems used in Texas, each suited to different soil types and property sizes. These include:
- Conventional Septic Systems: These systems use a septic tank and a soil absorption field.
- Aerobic Treatment Units (ATUs): These units introduce oxygen into the treatment process, promoting the breakdown of organic matter.
- Drip Irrigation Systems: These systems distribute treated wastewater through a network of tubing, ensuring even dispersal and reducing the risk of groundwater contamination.
- Mound Systems: Used in areas with high water tables or shallow soil bedrock, mound systems elevate the drain field above the natural soil surface.
Septic Design Regulations in Texas
State and Local Regulations
In Texas, the design and installation of septic systems are regulated by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ). Local counties may also have additional regulations. Key regulations include:
- Permitting: A permit is required for the installation of any septic system. This ensures the system meets state and local health and safety standards.
- Site Evaluation: A thorough site evaluation must be conducted to determine soil suitability, groundwater levels, and potential site limitations.
- System Sizing: The size of the septic system must be appropriate for the property’s size, soil type, and anticipated water usage.
Importance of Compliance
Compliance with these regulations is crucial to prevent health hazards, environmental contamination, and legal issues. Properly designed and maintained septic systems protect public health and preserve water quality.
Designing a Septic System in Texas
Site Assessment
A comprehensive site assessment is the first step in designing an effective septic system. This includes:
- Soil Testing: Soil permeability tests determine how quickly the soil can absorb water, influencing the design of the drain field.
- Topography: The land’s slope and natural drainage patterns impact system placement and design.
- Environmental Considerations: Proximity to water bodies, wells, and property boundaries must be considered to prevent contamination and ensure regulatory compliance.
Choosing the Right System
Selecting the appropriate septic system depends on various factors, including soil type, property size, and budget. Consulting with a professional septic service provider like Strictly Septic Service ensures that the chosen system meets all regulatory requirements and is tailored to the property’s specific needs.
Installation Process
Hiring a Professional
Professional installation is crucial for the longevity and efficiency of a septic system. Reputable companies, such as Strictly Septic Service, provide expert installation services, ensuring that the system is installed correctly and complies with all regulations.
Installation Steps
- Site Preparation: Clearing and grading the site to accommodate the septic system.
- Tank Installation: Excavating and placing the septic tank in the designated location.
- Drain Field Construction: Constructing the drain field according to the site plan and soil conditions.
- System Testing: Conducting final tests to ensure the system functions correctly and meets regulatory standards.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Routine Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential to keep septic systems functioning efficiently. Key maintenance tasks include:
- Regular Pumping: Septic tanks should be pumped every 3-5 years to remove accumulated solids.
- Inspections: Routine inspections help identify potential issues before they become major problems.
- Effluent Filters: Cleaning or replacing effluent filters prevents clogging and ensures smooth operation.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Common septic system issues include slow drains, unpleasant odors, and water pooling in the drain field. Addressing these issues promptly can prevent system failure and costly repairs. Strictly Septic Service offers expert troubleshooting and repair services to address any septic system problems efficiently.
Benefits of a Well-Designed Septic System
Environmental Protection
A well-designed septic system protects the environment by preventing groundwater contamination and ensuring proper waste treatment. Advanced systems like ATUs and drip irrigation systems enhance treatment efficiency and reduce the environmental footprint.
Cost-Effectiveness
Investing in a well-designed septic system can save property owners money in the long run. Properly maintained systems reduce the need for expensive repairs and extend the system’s lifespan.
Property Value
A reliable and efficient septic system can increase property value, making it an attractive feature for potential buyers. Ensuring that the system meets all regulatory requirements and functions efficiently adds to the property’s overall appeal.